- Building Supplies
- Electrical
- Smart Home, Security, Wi-Fi
- TV & Home Theater
- Extension Cords & Surge Protectors
- Electrical Wire & Cable
- Service Entrance Cables
- Primary Wire
- Sprinkler Wire
- Security Cables
- Armored Cable
- Power Cord
- Thermostat Wire
- Network & Data Cables
- XHHW Wire
- Specialty Wire & Cables
- Ground Wire
- Cable & Wire Holders
- Electrical Whips & Whip Kits
- Dual Armored Cable
- Non-Metallic Wire
- Landscape Lighting Cables & Connectors
- UF Wire
- TFFN & THHN Wire
- Speaker Wire
- Submersible Pump Cables
- Cable & Wire Connectors
- Wall Plates & Inserts
- Conduit & Conduit Fittings
- Generators
- Electronics
- Light Sockets & Adapters
- Electrical Outlets & Plugs
- Electrical Testers & Tools
- Batteries
- Fire Safety
- Light Switches & Dimmers
- Electrical Boxes & Covers
- Solar Power
- Doorbells
- Power Distribution & Circuit Protection
- Electrical Tape
- Lawn & Garden
- Garden Hoses & Accessories
- Landscaping & Hardscaping
- Outdoor Tools & Equipment
- Snow Blowers, Parts & Accessories
- Lawn & Garden Hand Tools
- Chainsaws & Pole Saws
- Spreaders & Sprayers
- Power Equipment Combo Kits
- Trimmers & Edgers
- Power Equipment Parts
- Lawn Aerators
- Engine Oil
- Wheelbarrows & Yard Carts
- Pressure Washers
- Snow Plows & Accessories
- Leaf Blowers
- Log Splitters
- Tillers & Cultivators
- Mulchers & Wood Chippers
- Axes & Mauls
- Power Equipment Fuel
- Garden Decor
- Outdoor Fountains
- Ponds
- Weathervanes
- Bird & Wildlife
- Garden Bridges
- Garden Arbors & Trellises
- Garden Fencing
- Well Pump Covers
- Garden Stakes & Shepherds Hooks
- Flags & Banners
- Outdoor Decorative Lanterns
- Garden Statues & Sculptures
- Outdoor Torches & Candles
- Thermometers, Clocks & Gauges
- Garden Stools
- Wind Chimes & Twisters
- Insect & Pest Control
- Pots & Planters
- Grills & Outdoor Cooking
- Irrigation & Outdoor Drainage
- Lawn Mowers
- Plant Care
- Storage & Organization
- Plumbing
- Water Heater Parts & Accessories
- Pipe & Fittings
- CPVC Pipe & Fittings
- Push to Connect Fittings
- Polyethylene Pipe, Fittings & Accessories
- Pipe Support & Clamps
- PEX Pipe, Fittings & Specialty Tools
- Tubing & Hoses
- Sewage Pipe & Fittings
- Structural Pipe & Fittings
- ABS DWV Pipe & Fittings
- Copper Pipe & Fittings
- CSST Pipe & Fittings
- Galvanized Pipe & Fittings
- Brass Fittings
- Pipe Insulation
- Black Pipe & Fittings
- PVC DWV Pipe & Fittings
- PVC Pipe & Fittings
- Water Filtration & Water Softeners
- Supply Lines
- Utility Sinks & Faucets
- Water Pumps & Tanks
- Valves & Valve Repair
- Water Heaters
- Plumbing Parts & Repair
- Augers, Plungers & Drain Openers
- Plumbing Tools & Cements
- Tools
- Air Tools & Compressors
- Hand Tools
- Clamps & Vises
- Hand Saws & Blades
- Taps & Dies
- Cutting & Crimping Tools
- Staple Guns & Riveters
- Multi-Tools
- Pliers & Plier Sets
- Punches & Knockout Punch Sets
- Sockets & Socket Adapters
- Maintenance Tools
- Powder Actuated Tools & Fasteners
- Ratchets & Breaker Bars
- Chisels & Pry Bars
- Mechanics Tool Sets
- Household Tool Sets
- Nut Drivers & Keys
- Files & Planes
- Grease Guns & Fittings
- Wrenches & Wrench Sets
- Hammers
- Screwdrivers
- Levels & Measuring Tools
- Drills & Drivers
- Clothing
- Ladders & Scaffolding
- Power Tools
- Safety
- Tool Storage & Work Benches
- Shop Vacuums & Accessories
- Flashlights
- Welding & Soldering
- Jobsite Radios
- Paint
- Heating & Cooling
- Furnaces & Furnace Accessories
- HVAC Duct & Fittings
- Registers & Grilles
- Thermostats
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Humidifiers & Dehumidifiers
- Air Conditioners & Fans
- Through Wall Fans
- Whole House Fan Shutters
- Ductless Mini Splits
- Blower Fans
- Portable Air Conditioners
- Evaporative Coolers
- Evaporative Cooler Accessories
- Whole House Fans
- Window Air Conditioners
- Wall Air Conditioners
- Wall Mounted Fans
- Central Air Conditioners
- Air Conditioner Parts & Accessories
- Portable Fans
- Whole House Fan Timers
- Air Filters & Accessories
- Air Purifiers & Accessories
- Portable & Space Heaters
- HVAC Components
- Heat Pumps
- Underfloor Heating
- Heating Fuel Tanks
- Radiator Covers
- Boilers
- Cleaning Supplies
- Hardware
- Cabinet Hardware
- Door Hardware
- Door Latch Hardware
- Door Security
- Closet Door Hardware
- Door Jamb Security & Repair Kits
- Pocket Door Hardware
- Screen & Storm Door Hardware
- Door Knockers
- Deadbolts
- Barn Door Hardware
- Door Sweeps
- Bathtub & Shower Door Hardware
- Sliding Patio Door Hardware
- Screen & Storm Door Handles
- Door Closers
- Door Handles
- Door Knobs
- Door Hinges
- Electronic Door Locks
- Door Kick Plates
- Door Stops
- Handlesets
- Picture Hangers
- Window Hardware
- Metal Rods, Shapes & Sheets
- Specialty Hardware
- Safes
- Furniture Hardware
- Fasteners
- Chains, Ropes & Tie-Downs
- Signs, Letters & Numbers
- Keys & Key Safes
- Locks
- Hooks
- Marine Hardware
- Automotive
- Lighting
- Flooring
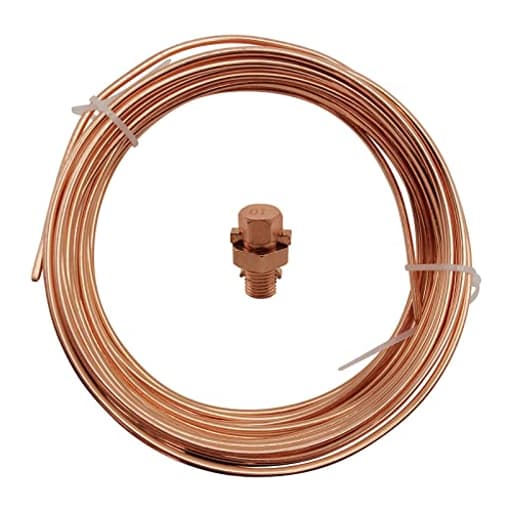
Ground wire is the safety backbone of any electrical system, providing a low-resistance path that carries fault current away from people and equipment so breakers trip fast and shocks, fires, and equipment damage are minimized. Whether you are wiring a residential panel, bonding metal enclosures on a commercial job, or installing lightning and surge protection, choosing the right grounding wire improves safety, performance, and code compliance.
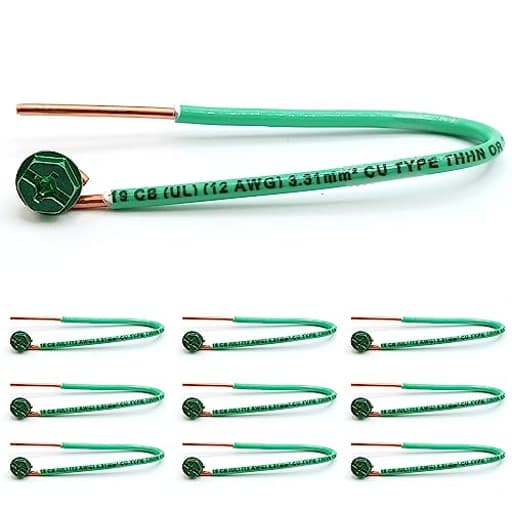
Common options include bare copper ground wire for maximum conductivity and corrosion resistance, green insulated THHN/THWN grounding wire for easy identification inside conduit, and aluminum grounding conductors for cost-sensitive runs when permitted by code. Select solid ground wire for fixed installations and stranded ground wire for flexibility in tight spaces or frequent vibration. Typical sizes range from 14 AWG for branch circuits to 4 AWG and larger for services, grounding electrode conductors, and bonding to rods, water pipes, and structural steel.
Benefits of quality grounding wire include faster fault clearing, stable reference for sensitive electronics, reduced electrical noise on audio/data lines, and improved surge and lightning dissipation. A well-planned equipment grounding conductor (EGC) network protects appliances, HVAC, EV chargers, generators, and shop tools.
Installation tips:
- Follow NEC and local codes for sizing, color, and routing.
- Keep runs as short and straight as practical; avoid sharp bends.
- Use listed clamps and lugs; clean metal for reliable bonding.
- Separate neutrals and grounds in subpanels; bond once at the service.
- Apply antioxidant on aluminum; protect buried conductors from corrosion.
- Test continuity and ground resistance to verify performance.
Shop spools and pre-cut lengths of copper ground wire, green insulated grounding wire, and accessories like ground rods, acorn clamps, split bolts, and grounding bars. Reliable, code-compliant grounding wire enhances electrical safety and keeps your projects running smoothly. Choose correct gauge for fault current.